Linux Deepin 15.2 Was Released With New Launcher Icons
Linux Deepin (formarly Hiweed GNU/Linux) is an open source and freely distributed operating system based on the Ubuntu Linux distribution and featuring its own desktop environment, theme, icons, and login manager.
Availability, boot options and system requirements
It is available for download as installable-only DVD ISO images, one for the 32-bit architecture and another one for 64-bit hardware platforms. The ISOs can be deployed to USB flash drives of 2 GB or higher capacity, as well as on blank DVD discs.
From the boot prompt, users can only install the operating system. Recommended system requirements include an Intel Pentium IV 2GHz processor or better, at least 1 GB of RAM (2 GB recommended for best performance), at least 10 GB of free disk space, a modern video graphics card from Intel, AMD or Nvidia, an AC97, SoundBlaster or HDA sound card, and a CD/DVD-ROM devices or USB port.
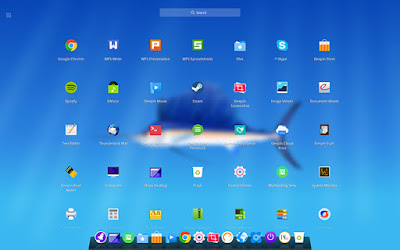
Linux deepin 15.2 continues the project’s vision on offering the community a gorgeous, well-designed, reliable, user-friendly, safe, secure, stable, and easy-to-use operating system for all ages and genre, by adopting a brand-new Launcher interface that promises to be more friendly and smarter, along with an intelligent search engine.
What’s new in Linux Deepin 15.2
Deepin Desktop:- Optimized desktop display, Computer and Trash icon are hidden by default (can be sent to desktop from Launcher);
- Desktop file renaming optimized, filename extension is not included by default;
- Fixed the issue that the upper-right hot corner-all windows can not be triggered;
- Removed the desktop application group function.
- Optimized Launcher interface at low resolution;
- Fixed the issue that some applications can not be uninstalled;
- Fixed the issue that the location displays abnormally for the small blue dot which occurs for newly installed applications;
- Fixed the issue that Launcher might froze.
- Optimized smart hidden;
- Fixed the issue that an excess of windows might overlap in classic mode;
- Fixed the issue that calendar displays abnormally after changing the date for the first time;
- Fixed the issue that application thumbnail displays abnormally;
- Fixed an issue that dock size displays abnormally in double screen mode.
- Simplified User Accounts module, removed the function that automatically change avatar after taken a photo;
- Simplified Personalization module, removed theme settings;
- Optimized display module to support custom settings of multi display;
- Optimized sound module to be uniformly controlled by the original sound effect switch;
- Optimized power module, the display is more intuitive and setting is convenient;
- Optimized Mouse and Touchpad module, added support of ThinkPad trackpoint;
- Fixed the issue that in Date and Time module, some existing time zones can not be deleted;
- Fixed the issue that system proxy abnormality in Network module;
- Fixed the issue that VPN connection abnormality in Network module.
- Optimized window animation effect;
- Added window menu settings;
- Fixed the issue that occurs in QQ emoji box.
- Fixed the issue that some machine black screen after inputting password;
- Fixed the issue that some shortcuts of blender conflict with system shortcuts;
- Fixed the issue that Deepin Screenshot & Deepin Movie can not be used on some machines;
- Fixed the issue that the system does not auto-mount removable hard disks.
Linux deepin 15.2 is available for download right now via our website as 64-bit and 32-bit ISO images, but if you are currently using the GNU/Linux operating system on your personal computer, you can get the new version by applying all the latest updates available in the software repositories.
Download Deepin 15.2 32 bit
Download Deepin 15.2 64 bit