How to Create Bootable USB For Ubuntu 16.10 ‘Yakkety Yak’ Using UnetBootin
“Yakkety Yak” is the code name for Ubuntu 16.10, scheduled for release October 2016. Yes, we’re talking about Ubuntu 16.10, which has been dubbed “Yakkety Yak” by Canonical founder Mark Shuttleworth on the day the company launched their sixth LTS (Long Term Support) release, Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus).
Ubuntu 16.10 Release Date
The release date for Ubuntu 16.10 is posted on the Ubuntu Wiki, along with the dates of the development milestones required to get it there.
Prior to the final stable release on October 22, the regular version of Ubuntu (i.e. the one flavors are based on) will take part in a single beta release tentatively set for September 22, 2016.
Ubuntu’s family of flavours, which includes Xubuntu and Ubuntu GNOME, will take advantage of more testing opportunities, with two alpha, two betas and a release candidate up for use.
- Alpha 1 – 30 June (for flavours)
- Alpha 2 – 28 July (for flavours)
- Feature Freeze — 18 August
- Beta 1 – 25 August (for flavours)
- UI Freeze — 8 September
- Final Beta – 22 September
- Kernel Freeze — 6 October
- Release Candidate – 13 October
The (draft) final release date of Ubuntu 16.10 Yakkety Yak is set for:
- Ubuntu 16.10 Final – October 20th
We’ve covered the entire development cycle of the Ubuntu 16.04 LTS operating system, and we’re planning on covering the one of the upcoming Ubuntu 16.10 OS too, keeping you guys informed of the new features that are about to be implemented as they’re revealed.
We took a quick look under the hood of the first 64-bit daily build Live ISO image of Ubuntu 16.10 (Yakkety Yak) to tell you what’s new, but there’s nothing new to report because it includes the same components that are available in the Ubuntu 16.04 ISOs.
Run UnetBootin on Windows 7,8,10
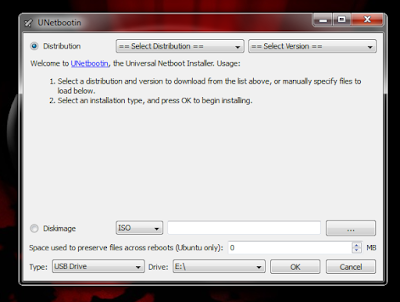
What is Unetbootin ?UNetbootin (Universal Netboot Installer) is a cross-platform utility that can create live USB systems and can load a variety of system utilities or install various Linux distributions and other operating systems without a CD.
Download Unetbootin For Windows
Select an ISO file or a distribution to download, select a target drive (USB Drive or Hard Disk), then reboot once done. If your USB drive doesn’t show up, reformat it as FAT32.
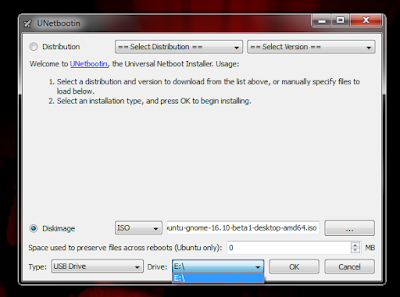
Select a Drive
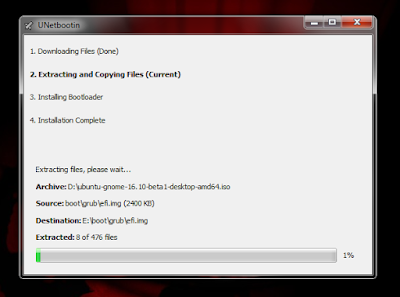
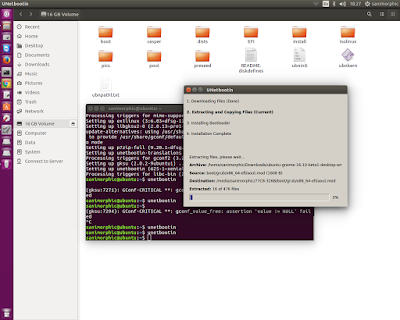
Push Ok Button and Wait a Few Minutes
After Etract is finished, reboot you computer and choose your USB for First booting.
Run UnetBootin on Linux Ubuntu :
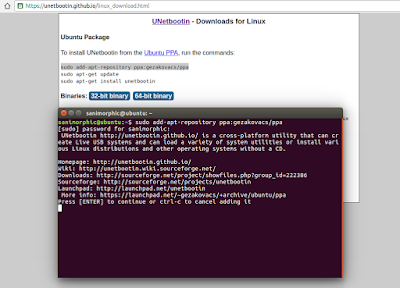
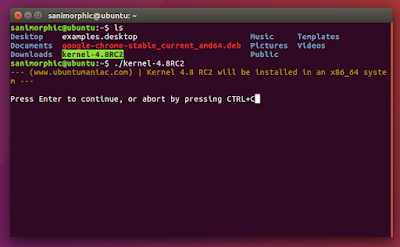
Install Unetbootin using PPA on Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus, Ubuntu 15.10 wily werewolf, Ubuntu 15.04 vivid Vervet, ubuntu 14.10 Utopic Unicorn, Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahr (LTS), Linux Mint 17.1, Linux Mint 17.2, Linux Mint 17.3 and other Ubuntu derivative systems, open a new Terminal window and bash (get it?) in the following commands:sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gezakovacs/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install unetbootinFor more download, you can follow this page.
Click Enter for continues installation
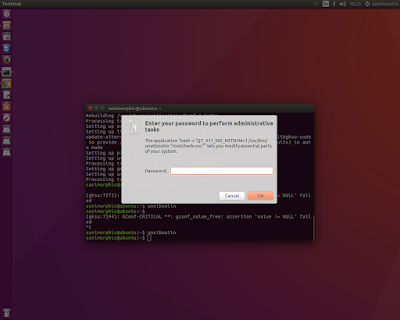
After installation is finished, run using this command :
$ unetbootinand ente the password root
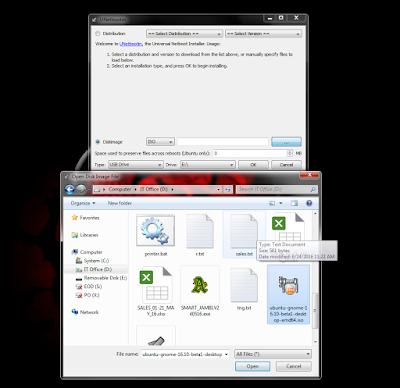
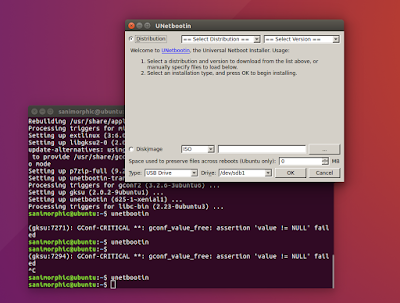
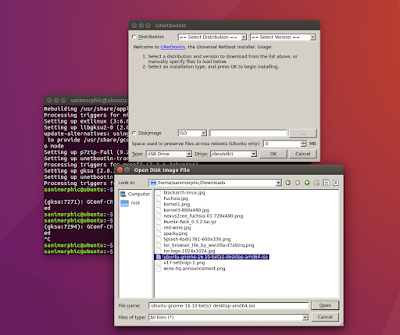
Click ISO and browse the ubuntu iso file, like this :
Choose, open and ok to create boot usb, like tihs
Enjoy! I hope this article adding you more clarity.