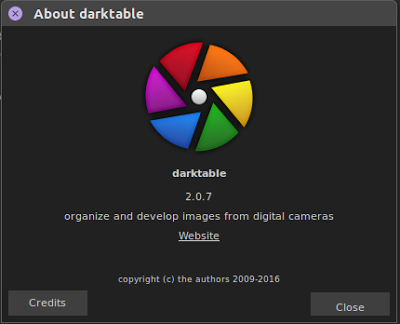
Darktable 2.0.7 is Released,Open-Source Image Editor Supports New Canon EOS 80D RAW Formats
Darktable is an open source application that provides both amateur and enthusiasts photographers with a virtual lighttable and darkroom that allows them to manage their digital negatives in a single and handy database. It has been designed from the ground up to be used for developing RAW images from digital cameras.
Lots of Nikon digital cameras now fully supported by darktable
Furthermore, darktable 2.0.7 fixes support for a large number of Nikon digital cameras, including Nikon 1 AW1, Nikon 1 J1 (12bit-compressed), Nikon 1 J2 (12bit-compressed), Nikon 1 J3, Nikon 1 J4, Nikon 1 S1 (12bit-compressed), Nikon 1 S2, Nikon 1 V1 (12bit-compressed), Nikon 1 V2, Nikon Coolpix A (14bit-compressed), Nikon Coolpix P330 (12bit-compressed), Nikon Coolpix P6000, Nikon Coolpix P7000, Nikon Coolpix P7100, Nikon Coolpix P7700 (12bit-compressed), and Nikon Coolpix P7800 (12bit-compressed).
The Nikon D1, Nikon D3 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed), Nikon D3000 (12bit-compressed), Nikon D3100, Nikon D3200 (12bit-compressed), Nikon D3S (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed), Nikon D4 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed), Nikon D5 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed), Nikon D50, Nikon D5100, Nikon D5200, and Nikon D600 (12bit-compressed) digital cameras are supported as well.
The list of supported Nikon digital cameras continues with the Nikon D610 (12bit-compressed), Nikon D70, Nikon D7000, Nikon D70s, Nikon D7100 (12bit-compressed), Nikon E5400, and Nikon E5700 (12bit-uncompressed) models. Unfortunately, the Nikon E8400, Nikon E8800, Nikon D3X (12-bit), and Nikon Df (12-bit) cameras are still not fully supported, so your help is needed (please contact the authors via the official website).
Last but not least, darktable 2.0.7 adds white balance preset support for Pentax K-70 and noise profile support for Sony DSC-RX10. The German and Catalan language translations have been updated, the application now shows if OpenEXR is supported or not (use the –version argument to find out), the app won’t crash if configured display profile is missing, and Histogram now displays the aperture with one digit after the dot.
Features at a glance
Key features include an astonishing graphical user interface designed for the modern computer user, support for importing single image files, folders, and scan for devices, ability to categorize images by numerous filters, such as ISO, color label, rights, creator, publisher, camera, date, time, title, lens, aperture, etc., as well as to access recently used collections.
In addition, the application lets users to view detailed information about an image, if available, such as lens, exposure, aperture, focal length, focus distance, ISO, model, maker, filmroll, image id, filename, version, full path, width, height, copyright, local copy, date, time, title, creator, latitude, and longitude.
It also features fully non-destructive editing, 4×32-bit floating point pixel buffers, GPU acceleration via OpenCL, built-in ICC profiles (sRGB, XYZ, linear RGB and Adobe RGB), zero-latency fullscreen mode, tethered shooting, flexible search functionality, powerful export system, and many translations.
The program is capable of importing a wide range of standard, RAW and HRD image formats, among which we can mention JPG, CR2, HDR, and PFM, and can export images to Picasa and Flickr, as well as to export to low dynamic range (JPEG, PNG, TIFF), linear high dynamic range (PFM, EXR) and 16-bit (PPM, TIFF) images.
Whats New Features on Darktable 2.0.7 :
New Features
- Filter-out some EXIF tags when exporting. Helps keep metadata size below max limit of ~64Kb
- Support the new Canon EOS 80D {m,s}RAW format
- Always show rendering intent selector in lighttable view
- Clear elevation when clearing geo data in map view
- Temperature module, invert module: add SSE vectorization for X-Trans
- Temperature module: add keyboard shortcuts for presets
Bugfixes
- Rawspeed: fixes for building with libjpeg (as opposed to libjpeg-turbo)
- OpenCL: always use blocking memory transfer hostdevice
- OpenCL: remove bogus static keyword in extended.cl
- Fix crash with missing configured display profile
- Histogram: always show aperture with one digit after dot
- Show if OpenEXR is supported in –version
- Rawspeed: use a non-deprecated way of getting OSX version
- Don’t show bogus message about local copy when trying to delete physically deleted image
Base Support (newly added or small fixes)
- Canon EOS 100D
- Canon EOS 300D
- Canon EOS 6D
- Canon EOS 700D
- Canon EOS 80D (sRaw1, sRaw2)
- Canon PowerShot A720 IS (dng)
- Fujifilm FinePix S100FS
- Nikon D3400 (12bit-compressed)
- Panasonic DMC-FZ300 (4:3)
- Panasonic DMC-G8 (4:3)
- Panasonic DMC-G80 (4:3)
- Panasonic DMC-GX80 (4:3)
- Panasonic DMC-GX85 (4:3)
- Pentax K-70
Base Support (fixes, was broken in 2.0.6, apologies for inconvenience)
- Nikon 1 AW1
- Nikon 1 J1 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon 1 J2 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon 1 J3
- Nikon 1 J4
- Nikon 1 S1 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon 1 S2
- Nikon 1 V1 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon 1 V2
- Nikon Coolpix A (14bit-compressed)
- Nikon Coolpix P330 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon Coolpix P6000
- Nikon Coolpix P7000
- Nikon Coolpix P7100
- Nikon Coolpix P7700 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon Coolpix P7800 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon D1
- Nikon D3 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed)
- Nikon D3000 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon D3100
- Nikon D3200 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon D3S (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed)
- Nikon D4 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed)
- Nikon D5 (12bit-compressed, 12bit-uncompressed)
- Nikon D50
- Nikon D5100
- Nikon D5200
- Nikon D600 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon D610 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon D70
- Nikon D7000
- Nikon D70s
- Nikon D7100 (12bit-compressed)
- Nikon E5400
- Nikon E5700 (12bit-uncompressed)
We were unable to bring back these 4 cameras, because we have no samples.
If anyone reading this owns such a camera, please do consider providing samples.
- Nikon E8400
- Nikon E8800
- Nikon D3X (12-bit)
- Nikon Df (12-bit)
White Balance Presets
Noise Profiles
Translations Updates
Install Darktable 2.0.7 on Ubuntu and Linux Mint Derivative System
Because it is
available via PPA, installing
Darktable 2.0.7 on Ubuntu 16.10 yakkety Yak, Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus, Ubuntu 15.10 Wily Werewolf, Ubuntu 15.04, Ubuntu 14.10 and derivative systems is easy. All you have to do is add the ppa to your system, update the local repository index and install the darktable package. Like this:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pmjdebruijn/darktable-release
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install darktable
to remove, do :
$ sudo apt-get remove darktable
For other linux distribution you can
follow this page
The source is available now. Binary packages are in the process of being built, and will appear soon at their respective
download locations.