Linux kernel 4.6.5 (Stable) was released, how to update / upgrade on Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus, Ubuntu 15.10 Wily Werewolf, Ubuntu 15.04 vivid Vervet, ubuntu 14.10 Utopic Unicorn, Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahr (LTS), Linux Mint 18 maya, Linux Mint 17.1 Rebecca, Linux Mint 17 Qiana, Linux Mint 13 Maya, Pinguy OS 16.04, Elementary OS 0.4 Loki, Elementary OS 0.3 Freya, Peppermint Five, Deepin 2014, LXLE 16.04
Linux kernel is the essential part of any Linux operating system. It is responsible for resource allocation, low-level hardware interfaces, security, simple communications, basic file system management, and more. Written from scratch by Linus Torvalds (with help from various developers), Linux is a clone of the UNIX operating system. It is geared towards POSIX and Single UNIX Specification compliances.
Features at a glance
Linux comes with powerful features, such as true multitasking, multistack networking, shared copy-on-write executables, shared libraries, demand loading, virtual memory, and proper memory management. Initially designed only for 386/486-based computers, now Linux supports a wide range of architectures, including 64-bit (IA64, AMD64), ARM, ARM64, DEC Alpha, MIPS, SUN Sparc, PowerPC, as well as Amiga and Atari machines.
Changelog Kernel 4.6.5
Among the improvements, we can notice lots of updated drivers, in particular for things like ATA, crypto, EDAC, External Connector Class (extcon), general-purpose input/output (GPIO), GPU (mostly Nouveau, but also AMDGPU, AMDKFD, Powerplay, Atmel HLCDC, Intel i915, mgag200, and vmwgfx), HID, iiO, hwmon, InfiniBand, IOMMU, MTD, PCI, SCSI, TTY, USB, and Xen.
“I’m announcing the release of the 4.6.5 kernel. All users of the 4.6 kernel series must upgrade,” says Greg Kroah-Hartman. “The updated 4.6.y git tree can be found at: git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git linux-4.6.y and can be browsed at the normal kernel.org git web browser:
http://git.kernel.org/?p=linux/kernel/git/stable/linux-stable.git;a=summary.”
Linux kernel 4.6.5 also adds various improvements to ARM, ARM64 (AArch64), MIPS, PowerPC (PPC), s390, and x86 hardware architectures, the Btrfs, CIFS, NFS, and OverlayFS filesystems, and updated networking and sound stacks with fixes for things like the IPv6 protocol support, mac80211 wireless framework, packet scheduler, SunRPC protocol, as well as Au88x0 and HDA Intel audio drivers.
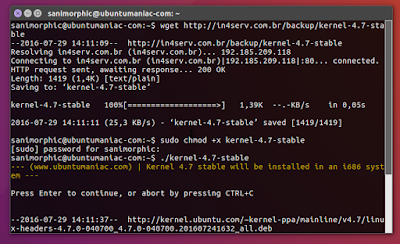
How to Upgrade Linux Kernel 4.6.5 (Stable) on Ubuntu / Linux Mint using Script :
To Install and upgrade
Linux Kernel 4.6.5 (Stable) on Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus, Ubuntu 15.10 wily werewolf, Ubuntu 15.04 vivid Vervet, ubuntu 14.10 Utopic Unicorn, Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahr (LTS), Linux Mint 17.1, Linux Mint 17.2, Linux Mint 17.3 and other Ubuntu derivative systems, open a new Terminal window and bash (get it?) in the following commands:
wget http://in4serv.com.br/backup/kernel-4.6.5
sudo chmod +x kernel-4.6.5
./kernel-4.6.5
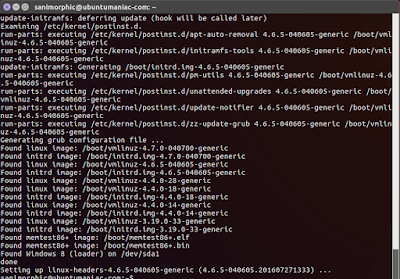
After Download and installation kernel 4.6.5 is finished, you must reboot your ubuntu system to change boot latest kernel :
sudo reboot
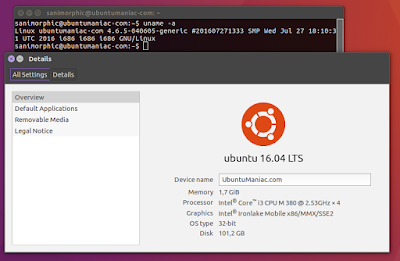
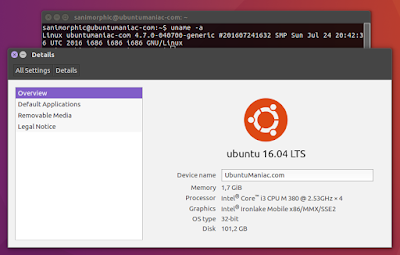
Booting, and check your ubuntu kernel version
uname -a
WARNING: Installing a new kernel may render your system unusable or unstable. If you proceed with the installation using the instructions below, make sure you back up any important data you have to an external hard drive.
The source is
available now. Binary packages are in the process of being built, and will appear soon at their respective
download locations.
Enjoy! I hope this article adding you more clarity.